max-height: 100%;
–left: 47.63%;
–top: 33.91%;
}

At times American history—and especially American Indian history—takes a dive down the rabbit hole with its twists and contradictions. The 1842 Cherokee Slave Revolt is one of those rabbit holes. The idea the Cherokee, or any tribe, owned slaves is not that alien a concept. For centuries before the arrival of Europeans on the continent American Indians had been enslaving captive enemies, and many tribes continued this practice well into the 1800s, much to the dismay of a paternal U.S. federal government. Each tribe had differing ideas on how to treat captives. Some regarded them, particularly young ones, as extended family members; others considered them disposable property. On an 1880 trip to Alaska with naturalist John Muir, Protestant Missionary S. Hall Young met one Huna Tlingit subchief who confessed to having ritually sacrificed two of his slaves, a husband and wife, in a bid to halt an advancing glacier.
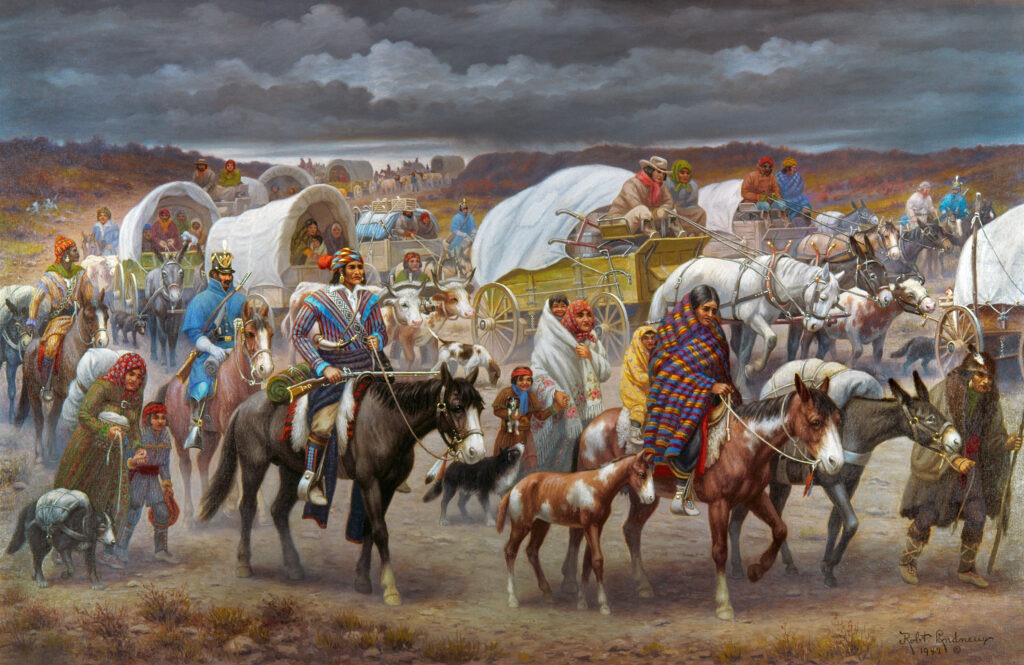
But the slaves at the center of the 1842 revolt were black men, women and children working Cherokee plantations and farms in Indian Territory (present-day Oklahoma). The breakout came less than four years after the last group of Cherokees had walked the Trail of Tears from their traditional homeland in Georgia to hinterlands of the southern Great Plains. President Andrew Jackson had ordered the forced march of some 16,500 Cherokees, a quarter or more of whom died en route (estimates range upward from 4,000 to as many as 8,000 fatalities). To transport such a vast number of people federal troops used 645 wagons, 5,000 horses and oxen, and a steamboat. The cost of the Cherokee removal came to $1,263,338 and 38 cents, which the government unabashedly deducted from the $4.5 million in federal funds promised to the tribe as reimbursement for its seized homelands.
Yet, in the midst of this human tragedy, another human tragedy was taking place. The Cherokees, for all their personal suffering, dragged along with them nearly 1,600 black slaves—the mobile human property that had been working their plantations and farms. En route to Indian Territory these slaves hunted game, gathered firewood and performed other chores, in many ways softening the blow of the trek for their Indian masters. Yet neither the Cherokee Nation nor the U.S. government recorded how many of the slaves perished en route.

Cherokee Plantations
The seeds by which the Cherokees would imitate their white neighbors had been laid years earlier in the wake of continuous warfare between them and first the British and then American forces. The wars left Cherokee towns in ruin and disarray, while a primary source of meat for the tribe, the whitetail deer population, crashed due to overhunting.
George Washington had evinced sympathy for American Indians since his youth as a surveyor on the Virginia frontier. As newly elected president of a nascent nation, he sought to work the concepts of tribal sovereignty and Indian assimilation into his economic plans. As tribal chiefs noted, Washington was a hard bargainer who seemed to covet their land, but not all of it. He also had a reputation among the chiefs as a fair man, and a generation of tribal males grew up with a “George” or “George Washington” in their names in honor of the man.
Washington took direct action to aid the Cherokees. His administration assisted in the rebuilding of their towns and sent agricultural agents to show the Cherokees how to successfully manage domestic animals and a variety of cash crops.
What changed the dynamics of the Southern economy was Eli Whitney’s invention of the cotton gin in 1793. Cotton was a labor-intensive crop to process. But Whitney’s invention eased the labor costs of cotton production. American growers duly increased their crop yield to satisfy European demands for cotton, and the resulting industry boom in the South lasted well beyond the Civil War.
Like fellow Southerners, Cherokee growers went for the money crop in a big way. They increased their tillage, then bought additional black slaves to satisfy the corresponding demand for labor. Soaring profits in turn led more than 200 Cherokees to start their own plantations.
With the influx of black slaves into their culture, the Cherokees in 1819 passed strict codes to forbid intermarriage with slaves, regulate the buying and selling of slaves, set punishments for runaways and prohibit slaves from owning property. Another period Cherokee law called for a fine of $15 against any master who allowed a slave to buy or sell alcohol.
GET HISTORY’S GREATEST TALES—RIGHT IN YOUR INBOX
Subscribe to our HistoryNet Now! newsletter for the best of the past, delivered every Monday and Thursday.
There were differences between the Cherokee plantations and those of Southern whites. Cherokee plantations had fewer slaves for their size, and the Cherokees themselves worked alongside their slaves in the fields. Their slaves were also permitted to grow food for their own consumption.
Cotton and tobacco were less than ideal crops, as they drained farmland of nutrients. That sparked an increasing demand for virgin land, in turn leading to the rapid settlement of what became Alabama and Mississippi. Before long Southern whites were eyeing the large tracts of uncultivated Cherokee lands immediately to their west. That the Cherokees also had black slaves infuriated whites trying to start their own plantations and farms. After all, slaves were a status symbol denoting economic success.
Starting with Thomas Jefferson, presidents looked for ways to reinterpret Washington’s concept of tribal sovereignty. In 1802 President Jefferson signed a compact with Georgia, paying the state $1.25 million for its western two-thirds (present-day Alabama and Mississippi) and committing the U.S. government to obtain title through purchase to all Indian lands within Georgia itself. No longer would federal power be the shield for tribes it had been. Jefferson then created government trading posts on Indian lands, extending unlimited credit to tribal leaders. Eventually the federal government demanded repayment of such debts in the form of more tribal land. After the 1803 Louisiana Purchase, Jefferson viewed the newly acquired region as a place Eastern tribes might be relocated. James Madison continued that policy. James Monroe initially sought to revert to Washington’s vision of relations between whites and Indian societies, though by his last year in office even he was calling for “Indian removal.” John Quincy Adams was likewise torn between the policies of assimilation and outright removal.
Then came the 1828 election of slave-owning Southern plantation owner and land speculator Andrew Jackson. In the colonial era Jackson had fought the Cherokee and every other major tribe in the Southeast and had personally profited from the sale of seized Cherokee lands. In 1830, at President Jackson’s urging, the Indian Removal Act passed the Senate 28–19 and the House of Representatives 101–97. In vain Cherokee leaders repeatedly visited the White House to ask Jackson to safeguard their property rights, including those governing their black slaves. Though the respective parties still needed to negotiate an actual removal treaty, most Cherokees saw the handwriting on the wall. Some 600 moved west to future Indian Territory on their own. Other Cherokees sought refuge in east Texas, in February 1836 signing a treaty with President Sam Houston, president of the newly independent republic. By the time the U.S. Congress ratified the Treaty of New Echota with the Cherokee Nation that spring, the tribe had split into four component bands.
Tensions Rise
Despite tensions between the Cherokees who had preceded most others to Indian Territory and those who later arrived on the Trail of Tears, the tribe as a whole rebounded surprisingly fast. The Cherokee Nation set up schools, a court system and law enforcement as individuals set to work establishing farms.
While most Cherokees lived on farmsteads in simple log cabins, more than 300 families started Southern-style plantations, living in two-story mansions and growing cotton using black slaves. The plantations ranged in size from 600 to 1,000 acres and put to work some 25 to 50 slaves. The Cherokees cultivated wheat, corn, hemp and tobacco and raised cattle and horses. Cotton remained king, however, and by 1840 the nation, thanks to its plantations, boasted a higher standard of living than that of neighboring Arkansas, Kansas or Missouri.

But tensions in the nation were on the rise. For one, it had become common knowledge among the Cherokee slaves that Mexico had abolished slavery in 1829. A decade later incoming Texas President Mirabeau Buonaparte Lamar drove the Cherokees from his republic. While most fled north into the Cherokee Nation as refugees, others crossed into Mexico. The number of blacks in the nation was also on the rise, not only through the purchase of additional slaves, but also with the arrival of runaway black slaves seeking refuge. Like their Southern white counterparts, however, the Cherokees only responded with a stricter slave code.
Adding to tensions was the manifest disparity between the lot of Cherokee slaves and those held by the Seminole. Seminoles passing through the Cherokee Nation in those years were technically captives from the ongoing Seminole wars in Florida en route to federally allotted lands farther west. Shipped up the Arkansas River from New Orleans, many disembarked at the Cherokee trading post of Webbers Falls to await transportation west. Striding down the riverboat gangplanks alongside their masters were flamboyantly dressed black Seminole slaves, many of whom bore arms. For Cherokee slaves witnessing their arrival, the blurred line between master and slave among the Seminoles must have been galling.
In the summer of 1842, given the rising prosperity the Cherokee Nation was enjoying, Sequoyah—the creator of the Cherokee alphabet, then in his 70s—led a small party into Mexico to find and return home with those Cherokees who had fled from Texas across the Rio Grande. He hoped for the unification of his people. (As it turned out, Sequoyah wouldn’t return home; he died in Mexico of a respiratory infection the next year.)
Whether inspired by the sight of the black Seminole slaves or the reawakened siren song of freedom in Mexico, slaves on the Cherokee plantations around Webbers Falls reached their threshold that fall. In years past black slaves had fled from their Cherokee masters back East and in Indian Territory, but only singly or in pairs. Dozens now waited for a signal.
Daring Escape
In the predawn darkness of November 15 the slaves on neighboring plantations rose quietly, made their way to their respective masters’ houses and overseers’ quarters, and barred the doors from the outside to ensure their occupants did not have an easy time getting out. Then they gathered at a predetermined rallying point for the planned breakout for Mexico.
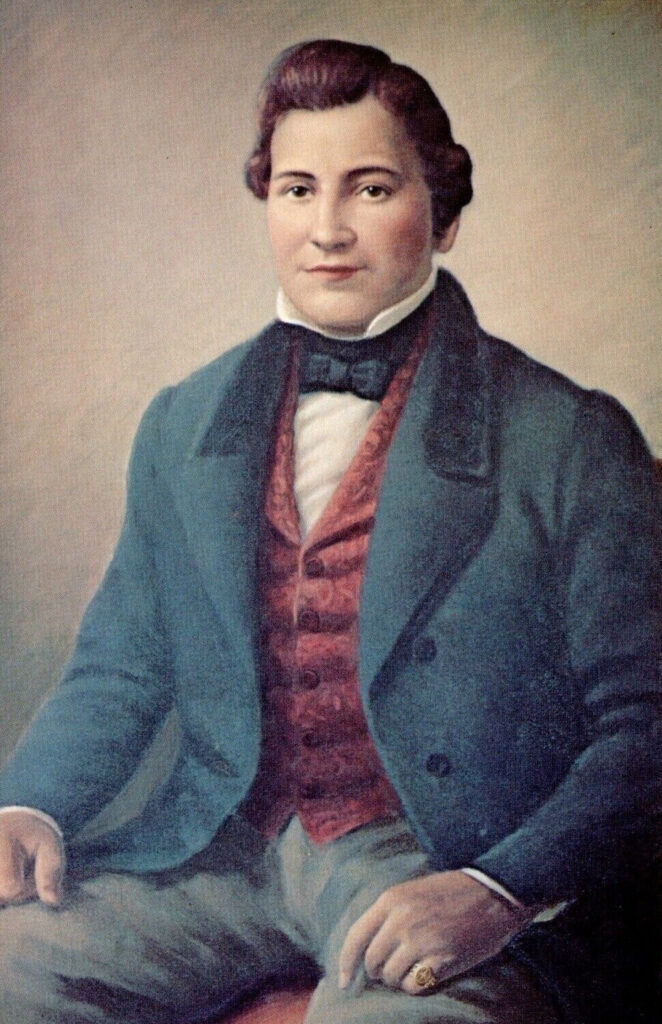

Most escapees hailed from the plantation of mixed-race Cherokee Joseph Vann. In 1834, after being evicted from his family estate in Georgia, Vann had established a large plantation in southeast Tennessee. Then, in 1837, a year before the main Cherokee removal, he preemptively moved to the newly relocated Cherokee Nation, settling on promising ground around Webbers Falls. On the backs of labor provided by 200 slaves, the Vann family prospered, ultimately holding title to thousands of acres ranging from the Kansas border to the southern boundary of the Cherokee Nation. The rich soil yielded consistently profitable crops of cotton and corn, which Vann plowed back into his ever-expanding holdings of land and slaves. By 1842 he had 300 slaves and even owned a steamboat, named Lucy Walker after a favorite thoroughbred.
On leaving their rallying point, the escapees made their way to Webbers Falls, where they broke into a store for supplies, weapons and ammunition. With the coming dawn many lost their nerve and scattered into the surrounding woodlands. The remaining 20 men, women and children headed southwest into the neighboring Creek Nation on stolen horses and mules. A few were riding Vann’s blooded racehorses.
Meanwhile, back on their plantations, the bewildered Cherokees finally broke out of their lodgings. There was no sign of their slaves. Mounted owners and overseers were soon scouring the countryside. As the patrols drove their wayward property from the woods individually and in small groups, it became apparent many were missing. On questioning the slaves, the Cherokees discovered the fugitives had struck out for Mexico.
Miles to the southwest, soon after the runaway Cherokee slaves crossed into the Creek Nation, 15 slaves from the Bruner and Marshall plantations joined them in the bid for freedom, swelling the party’s number to 35. On their heels galloped some 40 armed Cherokees with dogs, soon joined by a smaller party of Creeks equally determined to retrieve their property.
The combined Cherokee-Creek posse caught up with the fugitives in the Choctaw Nation, 10 miles south of the Canadian River. Spotting their approaching pursuers across the prairie, the runaways sheltered in a buffalo wallow big enough to hold them and their horses. Though few of the slaves had ever fired a gun, they decided to fight it out. In the ensuing skirmish the posse managed to kill two fugitives and recapture a dozen others. Fortunately for the remaining 21 escaped slaves, however, the firefight convinced the Cherokees and Creeks to turn back for reinforcements.
With no time to savor their victory, the fugitives continued their race south for Mexico.

Pursuit and Capture
The next day, 15 miles from the battle site, the fugitives happened across a pair of slave hunters wholly unaware of the breakout from the Cherokee Nation. James Edwards, who was white, and Billy Wilson, a Delaware, were transporting eight black captives—one man, two women and five children—belonging to a white man named Thompson who had married into the Choctaw Nation. In their own bid for freedom the Choctaw slaves had bolted west, hoping to link up with a Plains tribe, when another white in the nation spotted them and told Edwards and Wilson.
In a reversal of roles, however, the Cherokee and Creek runaways demanded Edwards and Wilson turn over their Choctaw captives. When the pair refused, the fugitives shot them. Though the five additional children would slow their progress, the party welcomed the Choctaws to join them on the road to Mexico. They would need to hurry, as their pursuers were regrouping.
On November 17 the Cherokee National Council authorized a company of tribal militiamen under the command of Captain John Drew to pursue, arrest and deliver the fugitive slaves to Fort Gibson, a U.S. Army post 20 miles north of Webbers Falls. The council also passed a resolution absolving the nation of any liability to the plantation owners if their runaway slaves were killed while resisting arrest. The Cherokee treasury would recompense Drew’s men for supplies and ammunition, while the commander at Fort Gibson loaned the captain 25 pounds of gunpowder.
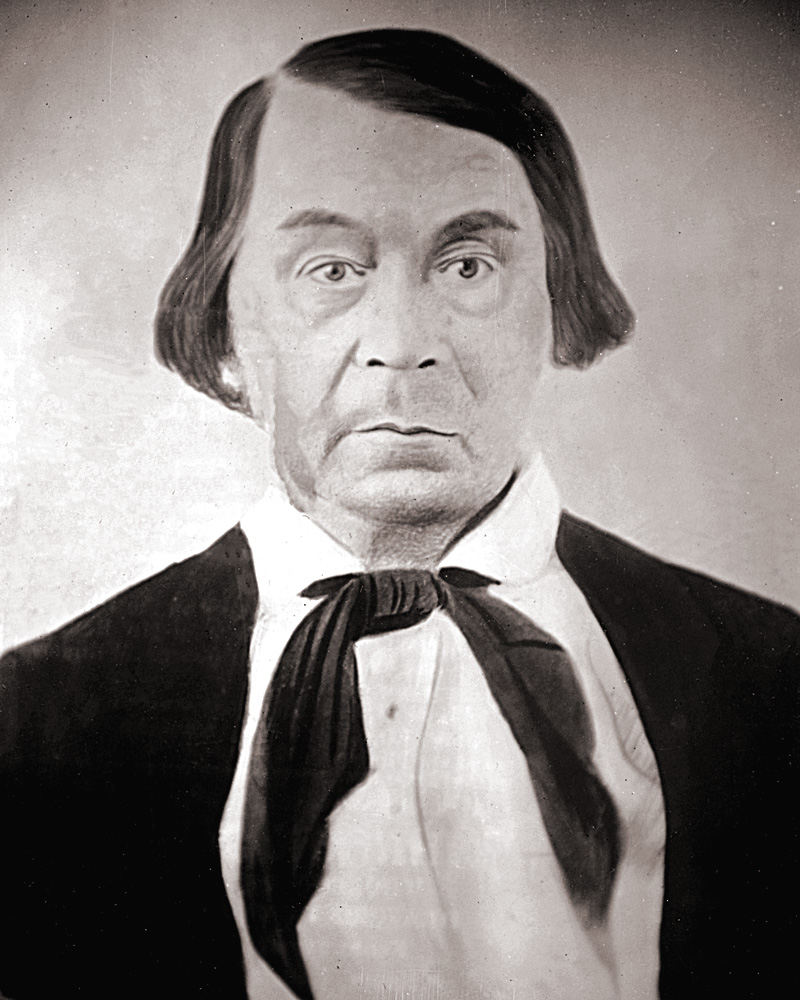

Captain Drew left Webbers Falls on November 21 with 87 well-armed militiamen. Arriving at the skirmish site in the Choctaw Nation on November 26, they picked up the fugitives’ trail and soon found the bodies of slave hunters Edwards and Wilson.
Two days later the Cherokee militia finally caught up with the runaways some 7 miles north of the Red River—the border between the United States and the Republic of Texas. Had they managed to cross it, the fugitives still would have had to traverse the expanse of slave-holding Texas to reach Mexico. But they had already run out of supplies and were starving.
The exhausted, dispirited fugitives offered no resistance. They must have picked up additional runaways, as Drew tallied 31 men, women and children, and two men off hunting remained at large. The militia and their captives reached Webbers Falls on December 7. The Cherokee National Council ordered five of the slaves held at Fort Gibson pending investigation into the killings of Edwards and Wilson, and two were tried for murder, though their cases appear to have been dismissed on technicalities. The Choctaw slaves were held until Cherokee authorities had determined Thompson’s claim to them.
The remaining Cherokee slaves were turned over to Vann, who put the runaways to work shoveling coal on his growing fleet of steamboats plying the Arkansas, Mississippi and Ohio rivers. In an instance of poetic justice, two years later a boiler explosion on one of his steamboats killed Vann.
Not the Last Struggle for Freedom
The 1842 revolt inspired other slaves to seek their freedom. Four years later Cherokee plantation owner Lewis Ross, a brother of Principal Chief John Ross, discovered his slaves had been collecting and hiding guns and ammunition. By 1851 nearly 300 blacks had attempted escape from plantations owned by members of the Five Civilized Tribes (Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek and Seminole). Most fugitives tried for Mexico, taking their chances with the slave hunters of Texas, while others headed north for the unorganized territory that in 1854 would become Kansas Territory, where slavery was prohibited.
True to form, the Cherokees reacted with stricter slave codes, expelled freedman from the nation and established a slave-catching or “rescue” company to prevent additional losses. Prior to the revolt such units comprised non-Cherokee slave hunters, like the pair killed by the fugitives in 1842. That changed in the wake of the revolt, as economically struggling Cherokees realized the money to be made catching and returning runaway slaves. The nation authorized them to charge any ammunition and supplies used in their hunts to the tribal treasury.
By the 1861 onset of the Civil War the Five Civilized Tribes held more than 8,000 black slaves, representing 14 percent of the population of Indian Territory. Members of the Cherokee Nation alone held 4,600 slaves.
An oddity in the Cherokee slave code held that blacks with even a trace of tribal ancestry were considered quasi members of the nation and thus granted certain rights, such as marriage into the tribe and the possibility of eventual citizenship. In 1847, when slavers kidnapped two such mixed-blood girls—whose father was Cherokee and mother was black—and took them across the border into Missouri, newspaper editorials within the nation demanded their return. Cherokee Sheriff Charles Landrum of the Delaware District took it on himself to enter Missouri with two deputies and rescue the girls before they could be sold. The Cherokee National Council financially reimbursed Landrum and his men for their daring “invasion” of Missouri.
Other blacks enslaved by the Cherokees weren’t as fortunate, at least until another president emancipated them on paper and hundreds of thousands of Americans spilled one another’s blood to affirm that proclamation.
For further reading on the topic author Mike Coppock recommends The Cherokee Nation: A History, by Robert J. Conley, and Ties That Bind: The Story of an Afro-Cherokee Family in Slavery and Freedom, by Miles Tiya.